What is Continuous Casting
Continuous casting is the intermediate link between steel making and rolling, an indispensable part of the metallurgical process, and an important part of the steel mill.
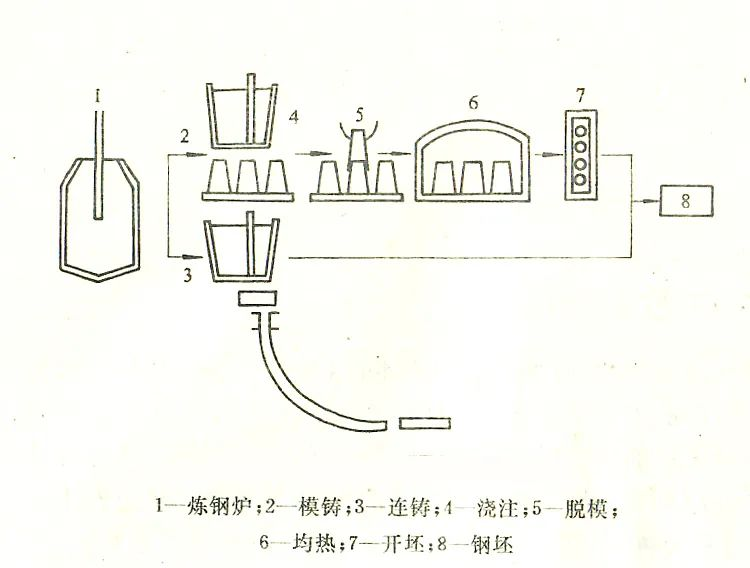
In the process of producing various types of steel products in steel mills, there are two methods of using steel solidification and forming: the traditional die casting method and the continuous casting method.
Die casting: a furnace steel intermittently poured into multiple ingots, to be solidified into shape after cooling off the mold to get cast billet. Because mold casting each pouring to do mold, cooling and then demold, covers an area of large, relatively long production efficiency is low.
Die casting has been produced for a long time, the production ratio is decreasing year by year. But at present, continuous casting can not completely replace die casting, for example, large cast and forged parts of nuclear power units, turbine rotors for hydropower, 10,000 tons of ship spindles and other large thickness special steel can only use die casting.
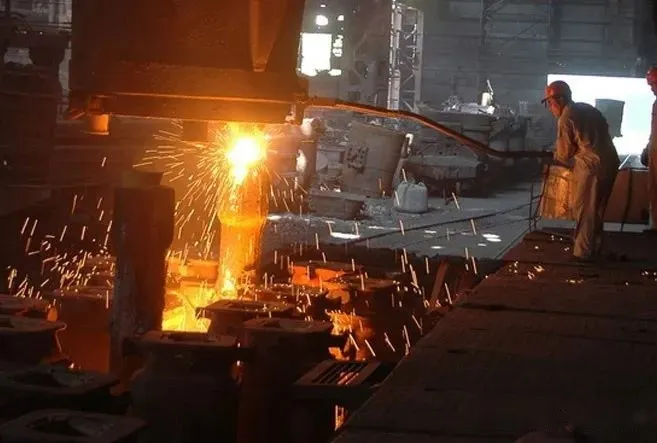
Continuous casting: The steel flows continuously into the intermediate ladle, and is injected into the crystallizer after mixing and shunting by the intermediate ladle to cool and solidify, resulting in an infinitely long cast billet, which can be directly used for rolling production after cutting.
Advantages and characteristics of continuous casting.
Simplifies the production process, eliminating the processes of mold casting, mold removal, mold rectification, ingot homogenization and billet opening, saving 40% in infrastructure investment, 30% in floor space, 40% in operating costs and 15% in refractory consumption.
Improved metal yield, significantly reducing the loss of billets by cutting the head and tail, which can increase the metal yield by about 9%.
Reduces energy consumption in the production process, eliminating the consumption of combustion power in the billet opening furnace, which can reduce energy consumption by 1/4 to 1/2.
Improves the mechanization and automation level of the production process.
Continuous casting process introduction
The process flow of continuous casting production is as follows
Ladle → intermediate ladle → crystallizer → secondary cooling → billet straightening → cutting → roller conveyor → billet transfer car (steel pusher) → billet casting
Core link.
Intermediate ladle (buffering, distribution)
Crystallizer (solidification forming)
Second cooling (cooling, guiding clamping)
Pulling and straightening machine (billet pulling, straightening)
Post time: Jan-06-2023